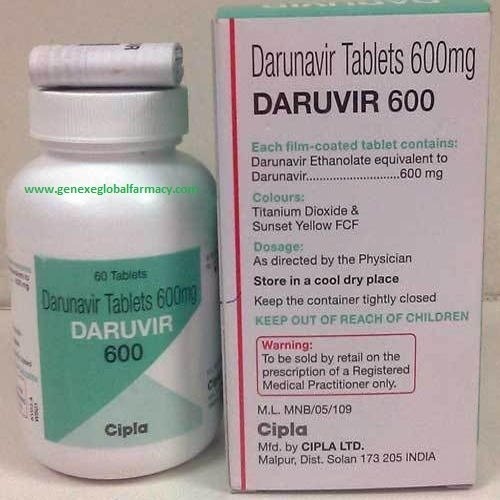
Darunavir Tablets
उत्पाद विवरण:
मूल्य और मात्रा
- 5
व्यापार सूचना
- प्रति सप्ताह
- दिन
- , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
उत्पाद वर्णन
Darunavir is an antiretroviral medication used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It belongs to the class of drugs known as protease inhibitors. Darunavir works by inhibiting the activity of the protease enzyme, which is necessary for the HIV virus to replicate and spread within the body.
Darunavir is typically available in tablet form, and the usual dosage for adults is 600 mg taken orally once daily with ritonavir 100 mg. Ritonavir is often used as a "booster" medication to increase the levels of darunavir in the body by inhibiting its metabolism. This combination is commonly used in HIV treatment regimens to enhance the effectiveness of darunavir.
It's important to take darunavir exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider and to not miss any doses. Skipping doses or not taking the medication as directed can lead to decreased effectiveness and potential development of drug resistance.
As with any medication, darunavir may cause side effects, and it's essential to be aware of these and report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider. Common side effects may include gastrointestinal disturbances, changes in liver function tests, and interactions with other medications.
If you have any questions or concerns about darunavir or its use, you should consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist for guidance. They can provide you with personalized advice based on your specific medical history and treatment needs.

Price: Â
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+



 संपर्क करें
संपर्क करें मुझे निःशुल्क कॉल करें
मुझे निःशुल्क कॉल करें
