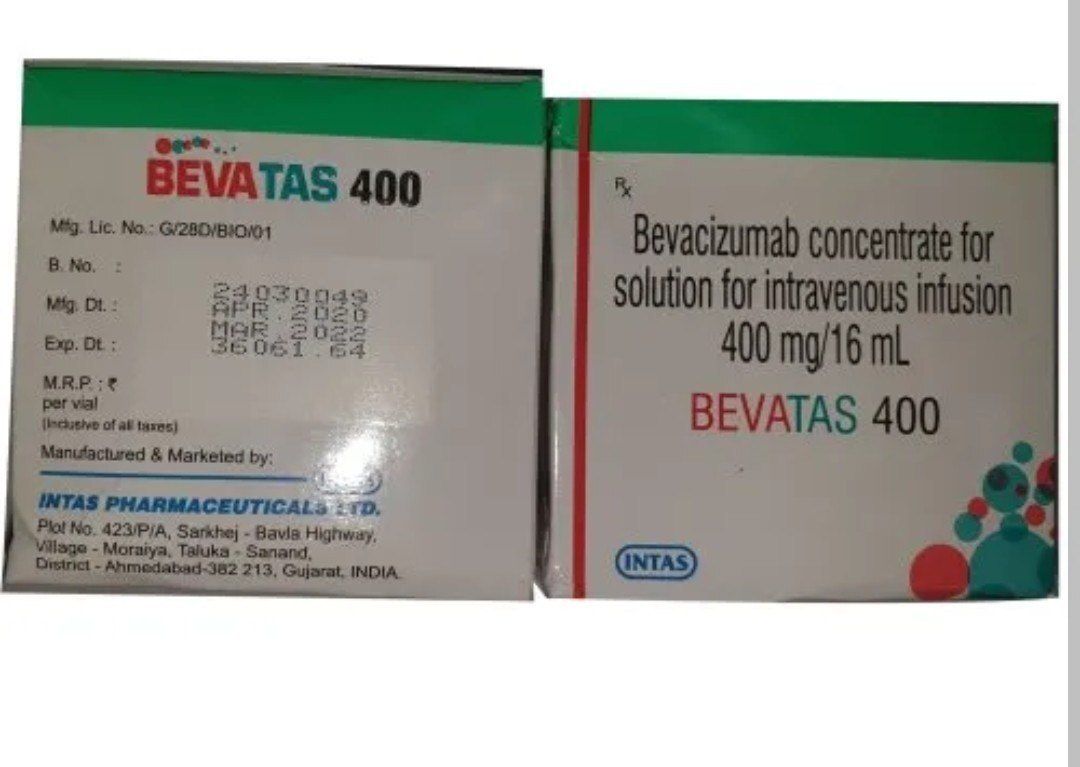
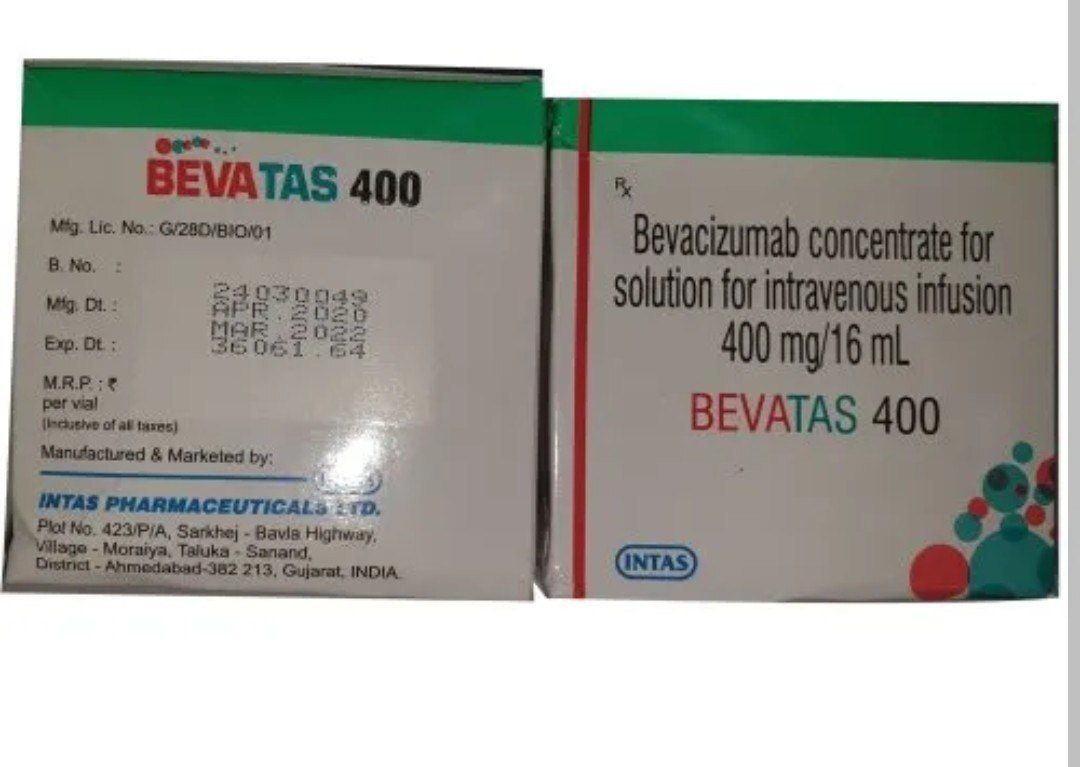
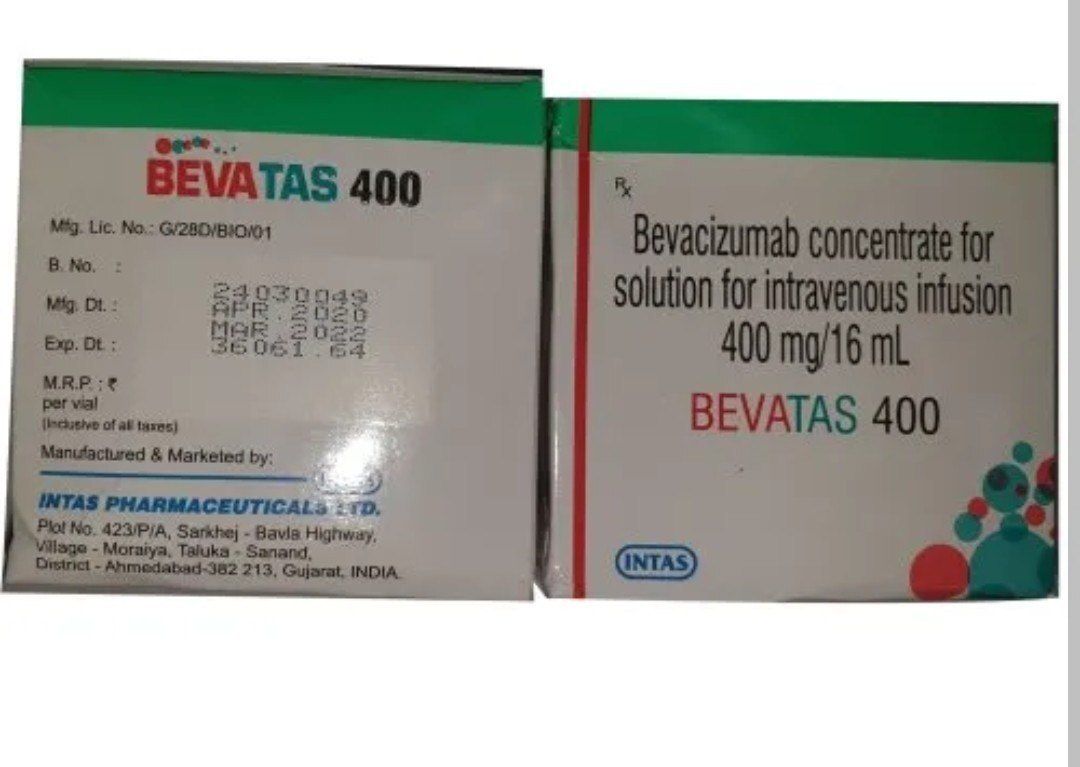
Bevacizumab Concentrate For Solution For Infusion
Product Details:
- Origin India
- Salt Composition Bevacizumab
- Dosage Form Concentrate for Solution for Infusion
- Indication Treatment of various cancers (colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, glioblastoma, renal cell carcinoma, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, etc.)
- Enzyme Types Not applicable (Monoclonal antibody)
- Feature Other
- Ingredients Other
- Click to View more
Bevacizumab Concentrate For Solution For Infusion Price And Quantity
- 9000.0 INR/Vial
- 5 Vial
- Monitor for infusion reactions, hypertension, thromboembolic events, and proteinuria during treatment.
- Compatible only with 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Do not use dextrose solution.
- Dilute with sodium chloride 0.9% prior to intravenous infusion. Do not administer as IV push or bolus.
- First infusion over 90 minutes; subsequent infusions may be administered over 60 or 30 minutes if tolerated
- Single-use glass vial with rubber stopper
- Carton containing single vial with patient information leaflet
- Prescription only medicine (Rx)
- 100 mg/4 mL and 400 mg/16 mL vials
Bevacizumab Concentrate For Solution For Infusion Product Specifications
- Other
- 24 Months
- Other
- Treatment of various cancers (colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, glioblastoma, renal cell carcinoma, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, etc.)
- Concentrate for Solution for Infusion
- Bevacizumab
- India
- Store at 2C to 8C. Do not freeze. Keep vial in outer carton to protect from light.
- Approximately 6.2
- Other
- Not applicable (Monoclonal antibody)
- Clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale brown liquid
- Monitor for infusion reactions, hypertension, thromboembolic events, and proteinuria during treatment.
- Compatible only with 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Do not use dextrose solution.
- Dilute with sodium chloride 0.9% prior to intravenous infusion. Do not administer as IV push or bolus.
- First infusion over 90 minutes; subsequent infusions may be administered over 60 or 30 minutes if tolerated
- Single-use glass vial with rubber stopper
- Carton containing single vial with patient information leaflet
- Prescription only medicine (Rx)
- 100 mg/4 mL and 400 mg/16 mL vials
Bevacizumab Concentrate For Solution For Infusion Trade Information
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- 1000 Vial Per Week
- 2 Days
- Asia, Australia, Central America, North America, South America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Middle East, Africa
- , All India, South India, Central India, West India, North India, East India, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chandigarh, Daman and Diu, Goa, Jharkhand, Odisha, Punjab, Assam, Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Nagaland, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Pondicherry, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
Product Description
Bevacizumab concentrate for solution for infusion, with a strength of 400 mg/16 mL, is a medication used in the treatment of various types of cancer. Here's an overview of its use:
1. Colorectal Cancer Bevacizumab is approved for use in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC). It is typically used in combination with a fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy regimen (such as FOLFOX or FOLFIRI).
2. Lung Cancer Bevacizumab is also used in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), specifically in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced, metastatic, or recurrent NSCLC. It may be used in patients who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
3. Breast Cancer Bevacizumab may be used in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, particularly in cases where the cancer is HER2-negative.
4. Renal Cell Carcinoma Bevacizumab, in combination with interferon alfa, is used for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer).
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein involved in the formation of new blood vessels that supply tumors with oxygen and nutrients. By inhibiting VEGF, bevacizumab helps to disrupt the blood supply to tumors, thereby slowing their growth and reducing their ability to spread.
The concentration of 400 mg/16 mL indicates that each mL of the solution contains 25 mg of bevacizumab. This solution is typically diluted further and administered as an intravenous infusion over a period of time specified by a healthcare professional.
Common side effects of bevacizumab may include hypertension (high blood pressure), proteinuria (protein in the urine), bleeding, gastrointestinal perforation, impaired wound healing, and increased risk of blood clots. It's important for patients to be monitored closely by their healthcare provider while receiving bevacizumab to manage any side effects and ensure the treatment remains effective.
As with any cancer treatment, it's crucial to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare professional to make informed decisions about treatment options.
How to Use Bevacizumab Concentrate Safely
Bevacizumab must be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride and administered as an intravenous infusion over a minimum of 90 minutes for the first dose. If tolerated, subsequent infusions may take 60 or even 30 minutes. Do not give as an IV push or bolus, and avoid mixing with dextrose solutions. Administration should occur in a hospital or clinical setting by qualified healthcare professionals.
What to Monitor During Treatment
Patients receiving Bevacizumab should be closely monitored for potential infusion reactions, hypertension, thromboembolic events, and proteinuria. Regular assessments will help ensure treatment tolerability and patient safety. Any side effects or unusual symptoms should be reported to the attending medical team promptly.
Benefits and Indications of Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab offers significant benefits for individuals with various cancers, such as colorectal, non-small cell lung, glioblastoma, renal cell carcinoma, cervical, and ovarian cancer. By inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), it helps slow tumor growth and progression, thus improving therapeutic outcomes in eligible patients.
FAQ's of Bevacizumab Concentrate For Solution For Infusion:
Q: How should Bevacizumab Concentrate for Solution for Infusion be prepared and administered?
A: Bevacizumab should be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride solution prior to intravenous infusion. It must never be administered as an IV push or bolus and should not be mixed with dextrose solutions. The first dose must be infused over 90 minutes; if tolerated, future infusions can be given over 60 or 30 minutes.Q: What precautions should be taken during Bevacizumab therapy?
A: Close monitoring for infusion reactions, hypertension, thromboembolic events, and proteinuria is essential during treatment. Administration should be carried out in a hospital or clinic by experienced medical personnel to ensure immediate care if adverse events occur.Q: When and where is Bevacizumab typically administered?
A: Bevacizumab is administered intravenously in hospital or clinical settings under the supervision of a healthcare professional, due to the need for dilution, correct infusion procedures, and monitoring for safety.Q: What is Bevacizumab used for and what are its main benefits?
A: Bevacizumab is indicated for treating several cancers including colorectal, non-small cell lung, glioblastoma, renal cell carcinoma, cervical, and ovarian cancers. By targeting VEGF, it helps to inhibit blood vessel growth in tumors, slowing cancer progression and improving treatment response.Q: How should Bevacizumab be stored prior to use?
A: Store Bevacizumab vials at 2C to 8C in their original outer cartons to protect from light. Do not freeze, and adhere to the shelf life of 24 months for unopened vials.Q: What does Bevacizumab contain and what does it look like?
A: Each vial contains Bevacizumab as the active ingredient, along with excipients such as phosphate buffer, polysorbate 20, and sterile water. The solution is clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale brown, and odorless.
Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+












 Contact Us
Contact Us
